ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
HUMAN PENDING ACTIVITIES CAN CAUSE CLIMATE CHANGE

Our world is facing a crisis, when it comes to a liveable climate. There are changes in the flow and cycle of life in the world where we live, and it also has an effect on the living organisms , surrounding it. People are bombarded by the questions “why is the weather is getting worse?”, “why the glaciers from the south is gradually melting?”, and why Catastrophies damaged homes and other imfrastrastractures vastly?”. Our current situation in commiting an environmental issues is weak, you totally don’t need any explanations and other portrations on it how would strive us people, simply reflect on what you see on your environment. Do you see changes?, do you see innovations yet?, you as an independent citizen is also working to save our nature in the name of the climate?. Then why you don’t take any actions to save the nature, why you don’t make any changes to sustain a liveable environment
Scientists stated that having a high confidence global temperature will continue to rise for decades to come, largely due to greenhouse gases produced by human activities. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which includes more than 1,300 scientists from the United States and other countries, forecasts a temperature rise of 2.5 to 10 degrees Fahrenheit over the next century. According to the IPCC, the extent of climate change effects on individual regions will vary over time and with the ability of different societal and environmental systems to mitigate or adapt to change. The IPCC predicts that increases in global mean temperature of less than 1.8 to 5.4 degrees Fahrenheit (1 to 3 degrees Celsius) above 1990 levels will produce beneficial impacts in some regions and harmful ones in others. Net annual costs will increase over time as global temperatures increase. “Taken as a whole,” the IPCC states, “the range of published evidence indicates that the net damage costs of climate change are likely to be significant and to increase over time.”
Droughts in the Southwest and heat waves (periods of abnormally hot weather lasting days to weeks) everywhere are projected to become more intense, and cold waves less intense everywhere. Summer temperatures are projected to continue rising, and a reduction of soil moisture, which exacerbates heat waves, is projected for much of the western and central U.S. in summer. By the end of this century, what have been once-in-20-year extreme heat days (one-day events) are projected to occur every two or three years over most of the nation.
If we do not make solutions and give recommendations, there is no even a change. Many studies have been done, there are many ways to minimize it, but it does not work much instead it is beneficial to other sectors. Can you call it innovation? if no changes occur. The global temparature is rising upon a year, can you sustain a liveable environment? Can you sustain a liveable climate?. Let us grow as a community let’s make a change for the sake of the environment, we can make a change if we have a discipline. Let us start to make a change.
References and citations
- IPCC 2007, Summary for Policymakers, in Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, p. 17.
- IPCC, 2013: Summary for Policymakers. In: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[Stocker, T.F., D. Qin, G.-K. Plattner, M. Tignor, S.K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex and P.M. Midgley (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.
- USGCRP 2014, Third Climate Assessment.
- USGCRP 2017, Fourth Climate Assessment.
INDUSTRIALIZATION AND ITS EFFECT ON THE ENVIRONMENT

Many of our needs come from factories and it also provides efficient and high quality products. But these factories also bring bad effects to the lives of the majority especially to our nature. In the passing years, where people brings changes in our society, the balance of our eco system is bonign and the living organisms in the environment start to extinct. Our ecological status is critically damaged because of the harmful effect of the human pending activities. We soar to have a good air to breathe, but it is still on the process of going back to the normal stage of having a conditioned atmosphere. In our current condition in our society, one of the significant environmental issue we face is the disadvantage of industrialization in our community.
With the coming of the Industrial Revolution, humans were able to advance further into the 21st century. Technology developed rapidly, science became advanced and the manufacturing age came into view. With all of these came one more effect, industrial pollution. Earlier, industries were small factories that produced smoke as the main pollutant. However, since the number of factories were limited and worked only a certain number of hours a day, the levels of pollution did not grow significantly. But when these factories became full-scale industries and manufacturing units, the issue of industrial pollution started to take on more importance.
Any form of pollution that can trace its immediate source to industrial practices is known as industrial pollution. Most of the pollution on the planet can be traced back to industries of some kind. In fact, the issue of industrial pollution has taken on grave importance for agencies trying to fight against environmental degradation. Countries facing sudden and rapid growth such industries are finding it to be a serious problem which has to be brought under control immediately. Industrial pollution takes on many faces.
It contaminates many sources of drinking water, releases unwanted toxins into the air and reduces the quality of soil all over the world. Major environmental disasters have been caused due to industrial mishaps, which have yet to be brought under control. Below are a few of the causes of industrial pollution that have resulted in environmental degradation.
The ecosystem has been significantly impacted because of pollution, and the consequence will affect many future generations. Big industries and manufacturing plants use significant amounts of water from nearby lakes, rivers, and oceans to operate. During the manufacturing process, the water is exposed to chemicals, heavy metals, organic sludge, and radioactive waste. That water is then dumped back into its original water source. Not only does this process affect the plants, animals, and insects in their habitat, farmers also use that water for irrigation, causing harmful effects to the food we eat. Water pollution has caused many different groundwater sources to be labeled as unsafe for people and animals alike. Once it is rendered dangerous, the only use for that water is for it to be reused in the plants that initially harmed it.
Industrial pollution continues to cause significant damage to the earth and all of its inhabitants. It disrupts natural habitats and rhythms, affecting wildlife and ecosystems. Animals are becoming extinct, and habitats are being destroyed. Pollution is the culprit for oil spills and radioactive material leaks, and both of those types of disasters take years to decades to clean up.
Reducing Industrial Pollution
As the harmful effects of industrial pollution increase, there are many agencies and individuals who are working to reduce carbon footprints and live and work eco-friendlier. Here are some of the different steps being taken to reduce and eliminate pollution:
- Development of better technology for waste disposal.
- Increased recycling efforts.
- Development of cooling rooms or bins that allow industries to recycle the water they need instead of pushing it back into the natural water source it came from.
- Adopting organic water and soil cleaning methods, like using microbes that feed off of metal and waste.
- Creating policies that prevent land misuse.
REFERENCE AND CITATION (External Link Included)
1. Conserve Energy Future (www.conserve-energy-future.com/causes-effects-of-industrial-pollution.php)
2. Conservation Institute (www.conservationinstitute.org/industrial-pollution/)
AIR POLLUTION AND ITS EFFECT TO THE HUMAN HEALTH

Air pollution is a mix of particles and gases that can reach harmful concentrations both outside and indoors. Its effects can range from higher disease risks to rising temperatures. Soot, smoke, mold, pollen, methane, and carbon dioxide are a just few examples of common pollutants. In the U.S., one measure of outdoor air pollution is the Air Quality Index, or AQI which rates air conditions across the country based on concentrations of five major pollutants: ground-level ozone, particle pollution (or particulate matter), carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen dioxide. Some of those also contribute to indoor air pollution, along with radon, cigarette smoke, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), formaldehyde, asbestos, and other substances.
Though many living things emit carbon dioxide when they breathe, the gas is widely considered to be a pollutant when associated with cars, planes, power plants, and other human activities that involve the burning of fossil fuels such as gasoline and natural gas. That’s because carbon dioxide is the most common of the greenhouse gases, which trap heat in the atmosphere and contribute to climate change. Humans have pumped enough carbon dioxide into the atmosphere over the past 150 years to raise its levels higher than they have been for hundreds of thousands of years. Other greenhouse gases include methane —which comes from such sources as landfills, the natural gas industry, and gas emitted by livestock—and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which were used in refrigerants and aerosol propellants until they were banned in the late 1980s because of their deteriorating effect on Earth’s ozone layer.
Another pollutant associated with climate change is sulfur dioxide, a component of smog. Sulfur dioxide and closely related chemicals are known primarily as a cause of acid rain. But they also reflect light when released in the atmosphere, which keeps sunlight out and creates a cooling effect. Volcanic eruptions can spew massive amounts of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere, sometimes causing cooling that lasts for years. In fact, volcanoes used to be the main source of atmospheric sulfur dioxide; today, people are. Airborne particles, depending on their chemical makeup, can also have direct effects separate from climate change. They can change or deplete nutrients in soil and waterways, harm forests and crops, and damage cultural icons such as monuments and statues.
Main causes of air pollution Emissions from different transport modes, the burning of fossil fuels, industrial production, forest fires, aerosol use and radiation fare some of the main causes of air pollution. Such sources of emissions liberate gases and substances that are toxic for human beings, the most harmful of which are: tropospheric ozone (O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), benzo(a)pyrene (BaP) and suspended particulate matter (PM). How does air pollution affect our health? Our physical and psychological wellbeing is affected differently by the kind of air pollution we are exposed to. There are many organs and bodily functions that can be harmed, the consequences including: Respiratory diseases Cardiovascular damage Fatigue, headaches and anxiety Irritation of the eyes, nose and throat Damage to reproductive organs Harm to the liver, spleen and blood Nervous system damage.
Reference and Citations (External Link Included)
1. National Geographic (www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/global-warming/pollution/)
2.Sustainability for all ( https://www.activesustainability.com/environment/effects-air-pollution-human-health/)
SOIL POLLUTION AND ITS EFFECT IN THE LIVING ORGANISMS
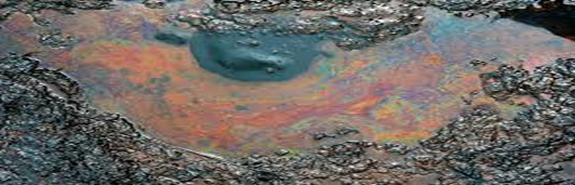
Soil pollution occurs when the presence of toxic chemicals, pollutants or contaminants in the soil is in high enough concentrations to be of risk to plants, wildlife, humans and of course, the soil itself. Arable land is turning to desert and becoming non-arable at ever-increasing rates, due largely in part to global warming and agricultural fertilizers and pesticides, lessening the hope that we can feed our booming population. Within 40 years, there will be over 2 billion more people, which is the equivalent of adding another China and India. Food production will have to increase at least 40% and most of that will have to be grown on the fertile soils that cover just 11% of the global land surface. However, there is little new land that can be brought into production and existing land is being lost and degraded. The United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization states that annually, 75 billion tons of soil, the equivalent of nearly 10 million hectares, which is about 25 million acres, of arable land is lost to erosion, water-logging and salination and another 20 million hectares is abandoned because its soil quality has been degraded. Contact with contaminated soil may be direct, from using parks, schools etc., or indirect by inhaling soil contaminants which have vaporized or through the consumption of plants or animals that have accumulated large amounts of soil pollutants, and may also result from secondary contamination of water supplies and from deposition of air contaminants
Main Causes of Soil Pollution
– Industrial wastes such as harmful gases and
chemicals, agricultural pesticides, fertilizers and insecticides are the most
common causes of soil pollution.
– Ignorance towards soil management and related
systems.
– Unfavorable and harmful irrigation practices.
– Improper
septic system and management and maintenance of the same.
– Leakages
from sanitary sewage.
– Acid
rain, when fumes released from industries mix with rain.
– Fuel
leakage from automobiles that get washed away due to rain and seep into nearby
soil.
– Unhealthy waste management techniques, which
are characterized by release of sewage into the large dumping grounds and
nearby streams or rivers.
Types of Soil Pollution
Land pollution from domestic and industrial solid waste
Electronic goods, broken furniture, junk papers, polythene bags, plastic cans, bottles, wastewater, toxic waste from the hospital etc. are examples of solid waste which pollute the soil. Most of this litter is non biodegradable. These wastes affect the soil structure by being blocked in it for long periods. Because these solid wastes do not decay easily, they lie on landfill sites for thousands of years and keep polluting the soil and the environment continuously. In addition to the soil, humans and animals living around these landfill sites are greatly harmed.
Household waste, industrial waste etc. contain residues of harmful toxic inorganic and organic chemicals. In these residues, radiation elements such as strontium, cadmium, uranium, ladders are found, which affect the vitality and fertility of the land. Fly ash is a major source of pollution surrounding the industrial area. There are chemicals or other types of waste in industries, which are dumped at some place. So much so that soil becomes polluted and trees and plants do not even grow in such a part.
Soil pollution by chemical substances
The use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers has increased for cultivating more crops and these pollutants are making the soil poisonous and in many places the soil has become dead due to excessive use of it.
Producers of fertilizers, insecticides, pesticides, pharmaceuticals produce a lot of solid and liquid waste. Due to leaks from pipes and gutters, pollutants also go into the soil and spread pollution In the chemical and nuclear power plants, a large amount of waste is released continuously and due to the absence of proper arrangements for their storage and disposal, these substances pollute the soil.
In commercial agriculture, insecticides are being used indiscriminately and inorganic chemical fertilizers are also being used day by day. The chemical fertilizers are polluting the environment and groundwater resources of phosphate, nitrogen and other organic chemical land. The most dangerous pollutants are bioactive chemicals, due to which the micro-organisms of climates and other soil are being destroyed resulting in decreased quality of soil. Toxic chemicals enter the diet chain, so that they reach the top consumer. Bioactive chemicals are also called Creeping Deaths. In the last 30 years, the use of organic chemicals has increased by more than 11 times. India alone is using 100,000 tonnes of bio-chemicals per annum.
Continuous deforestation
Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the air; provide oxygen for humans and other organisms. Apart from these, tree plantations are also helpful in prevention of soil pollution and erosion. Tree plantation rejuvenates the lost potency of soil. But unfortunately, we are continuously cutting trees on the millions of acres of land for the wood required for construction and the land required for the cultivation, besides mining work.
Effects os Soil Pollution on Human Lives
More than 70% of the soil pollutants are carcinogenic in nature, intensifying the chances of developing cancer in the humans exposed to the polluted soils. Long-term exposure to benzene and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), for instance, is linked to the development of leukemia and liver cancer respectively. Soil pollutants can also cause skin diseases, muscular blockage, and central nervous system disorders.
Humans can be affected indirectly due to bioaccumulation or food poisoning. It happens when people consume crop produce that is grown in the polluted soils or when they consume animal products that eat plants from polluted soils. As a result, humans suffer from acute illnesses and may experience premature death.
Effects of Soil Pollution on the Environment
When soils are repeatedly contaminated and accumulate large amounts of poisonous materials and chemicals, the soil reaches a point where it cannot support plant life. Soil pollutants interfere with soil chemistry, biology, and structure. When these changes occur, beneficial soil bacteria, soil microorganisms, soil nutrients, and soil chemical processes begin to deteriorate to an extent where they diminish soil fertility. The ecological balance is lost completely. On this basis, the soil becomes unsuitable for crop survival or any other form of vegetation. If the plants die, then it means animals dependent on the plants will also die. This leads to migration of the larger animals and predators to other regions to find food supply, gradually leading to a reduction in wildlife and extinction. Soil pollution can as well change plant metabolism and lower crop productivity. Besides, when plants take up the soil contaminants, they pass them up the food chain, endangering the health of animals and humans.
Reference and citation ( External link included)
1. Everything Connects. Org (www.everythingconnects.org/soil-pollution.html)
2. Help Save Nature (www.helpsavenature.com/soil-pollution-causes-effects)
3. India Celebrating (www.indiacelebrating.com/environmental-issues/soil-pollution/)
Main Author of the article: Sujeet Kumar (prolific and versatile journalist with more than 10 years of experience in reporting and writing. Passionate about journalism and the other areas of communications, he has extensively written on a wide range of topics and issues for India’s leading publications. A Master in Mass Communication from GJU and Bachelor of Arts from University of Delhi, he has also handled desks, besides contributing to regular columns at various journalistic organisations)
4. Earth Eclipse (www.eartheclipse.com/pollution/devastating-effects-of-soil-pollution.html)
Main Author of the article: Sonia Madaan (Sonia is a High School Graduate and Runs the Writing and Editing Team for EarthEclipse.com. She is Extremely Passionate about Environment, Technology and Computing.)
IMPACT OF DEFORESTATION IN THE ENVIRONMENT

One of the main cause of deforestation is agriculture (poorly planned infrastructure is emerging as a big threat too) and the main cause of forest degradation is illegal logging. We’re losing 18.7 million acres of forests annually, equivalent to 27 soccer fields every minute.
Deforestation is a particular concern in tropical rain forests because these forests are home to much of the world’s biodiversity. In the Amazon around 17% of the forest has been lost in the last 50 years, mostly due to forest conversion for cattle ranching. Deforestation in this region is particularly rampant near more populated areas, roads and rivers, but even remote areas have been encroached upon when valuable mahogany, gold, and oil are discovered.
Farming, grazing of livestock, mining,
and drilling combined account for more than half of all deforestation. Forestry practices, wildfires and,
in small part, urbanization account for the rest. In Malaysia and Indonesia,
forests are cut down to make way for producing palm oil, which can be found in everything from shampoo to saltines. In the Amazon, cattle ranching and
farms particularly soy
plantations are key culprits.
Logging operations, which provide the world’s wood and paper products, also
fell countless trees each year. Loggers, some of them acting illegally, also build roads to access more and
more remote forests which
leads to further deforestation. Forests are also cut as a result of growing
urban sprawl as land is developed for homes.
Not all deforestation is intentional. Some is caused by a combination of human and natural factors like wildfires and overgrazing, which may prevent the growth of young trees.
Deforestation is considered to be one of the contributing factors to global climate change. According to Michael Daley, an associate professor of environmental science at Lasell College in Newton, Massachusetts, the No. 1 problem caused by deforestation is the impact on the global carbon cycle. Gas molecules that absorb thermal infrared radiation are called greenhouse gases. If greenhouse gases are in large enough quantity, they can force climate change, according to Daley. While oxygen (O2) is the second most abundant gas in our atmosphere, it does not absorb thermal infrared radiation, as greenhouse gases do. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most prevalent greenhouse gas. CO2 accounts for about 82.2 percent of all U.S. greenhouse gas, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Trees can help, though. About 300 billion tons of carbon, 40 times the annual greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels, is stored in trees, according to Greenpeace.
The deforestation of trees not only lessens the amount of carbon stored, it also releases carbon dioxide into the air. This is because when trees die, they release the stored carbon. According to the 2010 Global Forest Resources Assessment, deforestation releases nearly a billion tons of carbon into the atmosphere per year, though the numbers are not as high as the ones recorded in the previous decade. Deforestation is the second largest anthropogenic (human-caused) source of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere (after fossil fuel combustion), ranging between 6 percent and 17 percent, according to a study published in 2009 in Nature.
Carbon isn’t the only greenhouse gas that is affected by deforestation. Water vapor is also considered a greenhouse gas. “The impact of deforestation on the exchange of water vapor and carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and the terrestrial land surface is the biggest concern with regard to the climate system,” said Daley. Changes in their atmospheric concentration will have a direct effect on climate.
Deforestation has decreased global vapor flows from land by 4 percent, according to an article published by the journal National Academy of Sciences. Even this slight change in vapor flows can disrupt natural weather patterns and change current climate models.
Reference and Citation ( External Link Included)
1. World Wildlife Organization (www.worldwildlife.org/threats/deforestation-and-forest-degradation)
2. National Geographic (www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/global-warming/deforestation/)
3. Live Science (www.livescience.com/27692-deforestation.html)
ILLEGAL MINING

Destructive cases of illegal mining across the world
In South America, the $2.4 billion illegal gold mining industry has been destroying the Amazon and costing dozens of lives. In Peru, Bolivia, and Colombia, illegal gold mining operations by private companies have devastated local communities. The operations have left behind pools of cyanide and mercury, twice the size of Olympic swimming pools. In just three months, the illegal mining activities damaged the ecosystem by killing the entire fish population of the Aguita River after water-pumping machines leaked toxins into the water.
According to Colombia’s National Planning Department, Colombia now ranks second in the world for mercury pollution. Local populations have reported health issues related to mercury poisoning such as tremors and memory loss. According to some sources, illegal mining companies often extorted the local populations by forcing them to search for gold by sending in armed groups to intimidate them. Other times, they tried to barter deals by promising to repair crippling infrastructure in the region, but instead, pillaged the region and left without keeping their word. South America isn’t the only region that has suffered from illegal mining.In Africa, the conflict diamond industry cost thousands of lives in the 1990’s and 2000’s. During that time, the illegal industry produced billions of dollars which were used to fund civil wars that decimated countries including Sierra Leone, Angola, Liberia, Ivory Coast and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
Reference and Citation: Greentumble
(https://greentumble.com/the-dangerous-effects-of-illegal-mining/)
Mining can be defined as “the extraction of minerals and other geological materials from the earth.” Minerals and materials commonly targeted by mining include: base metals (e.g., copper, nickel), precious metals (e.g., gold, silver), iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock salt, and potash. The activity is deeply entwined with human history, with the oldest known mine dating back to over 40,000 years ago.
Mining is widely recognized as carrying significant risks of ecosystem destruction, environmental pollution, and worker injury, so “illegal mining” can be defined statutorily as violations of both specialized laws and regulations for mining, and more general laws and regulations that protect the environment and human welfare. From a more biocentric or ecocentric philosophical perspective, even statutorily legal mining might be considered a crime as minerals and other geological materials are nonrenewable, their mining can seriously impact the environment, and many minerals and materials are not recycled, even though they often can be. However, for the rest of this primer, I’ll just consider ‘illegal mining’ from a statutory, rather than philosophical, perspective.
Reference and Citation: Sustainably Enforced
Writer credits: Mark Gibson ( In-Focus:Illegal Mining Around the Globe)
(https://www.sustainablyenforced.org/news-and-analysis/globalillegalmining)
Adorning oneself with jewelry especially gold has been consistent across religions, cultures, class and gender. Unquestionably humans have a need for jewelry, but what precisely is this need?
Jewelry has served as a store of value to be converted to cash in times of need.Many individuals, institutions and countries across the world hold investments in gold bullion as financial backing.
Mining involves the activity, occupation and industry concerned with the extraction of minerals from the earth.
From electronic manufacturing companies to dental rooms gold and other precious metals are being used for various purposes. Gold has a positive impact on a nation’s GDP and it also create job opportunities for the community.In Ghana,the Mining industry accounts for 5% of the country’s GDP and minerals takes up 37% of the total export with gold accounting for 90% of the mineral export. Ghana is the second largest gold producer in Africa.
Notwithstanding the fact that the mining sector contributes to government revenue it also has serious negative impact on the environment and to miners.
The illegal mining sector in Ghana is plagued by several environmental and health problems. Several accidents have occurred and in some cases this has led to fatalities in the mines. In April 2013, at least 17 people were killed while mining illegally at a disused gold mine in Ghana’s central region. The ground caved in on the miners as they searched for gold deposits. Another serious impact is the health hazards as a result of pollution from gases, noise, dust and polluted water.
Coal mines release methane which can pollute the air.Sulphuric acid are utilized in the mining operations which drain into the water bodies, and adversely affect ground water. The movements of rock in the case of surface mining impact the land negatively. Craters are left in the areas where mining activities took place, destroying landscape and lush vegetation in the process. Deforestation is resulting in changes in the ecosystem which includes increasing the levels of Carbon Dioxide in the air.
Reference (External Link) (https://www.eoi.es/blogs/mavisasare/2014/01/14/illegal-mining-and-the-environment-%E2%80%93-ghana/)